OAK相机如何将YOLOv6模型转换成blob格式?(2.0 及之后版本)

▌.pth 转换为 .onnx
使用下列脚本(将脚本放到 YOLOv6 根目录中)将 pytorch 模型转换为 onnx 模型,若已安装 openvino_dev,则可进一步转换为 OpenVINO 模型:
示例用法:
python export_onnx.py -w <path_to_model>.pt -imgsz 640 export_onnx.py :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import argparse
import json
import logging
import sys
import time
from io import BytesIO
from pathlib import Path
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0]
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT))
from yolov6.layers.common import *
from yolov6.models.efficientrep import (CSPBepBackbone, CSPBepBackbone_P6,
EfficientRep, EfficientRep6)
from yolov6.models.effidehead import Detect
from yolov6.models.yolo import *
from yolov6.utils.checkpoint import load_checkpoint
try:
from rich import print
from rich.logging import RichHandler
logging.basicConfig(
level="INFO",
format="%(message)s",
datefmt="[%X]",
handlers=[
RichHandler(
rich_tracebacks=False,
show_path=False,
)
],
)
except ImportError:
logging.basicConfig(
level="INFO",
format="%(asctime)s\t%(levelname)s\t%(message)s",
datefmt="[%X]",
)
class YoloV6BackBone(nn.Module):
"""
Backbone of YoloV6 model, it takes the model's original backbone and wraps it in this
universal class. This was created for backwards compatibility with R2 models.
"""
def __init__(self, old_layer, uses_fuse_P2=True, uses_6_erblock=False):
super().__init__()
self.uses_fuse_P2 = uses_fuse_P2
self.uses_6_erblock = uses_6_erblock
self.fuse_P2 = old_layer.fuse_P2 if hasattr(old_layer, "fuse_P2") else False
self.stem = old_layer.stem
self.ERBlock_2 = old_layer.ERBlock_2
self.ERBlock_3 = old_layer.ERBlock_3
self.ERBlock_4 = old_layer.ERBlock_4
self.ERBlock_5 = old_layer.ERBlock_5
if uses_6_erblock:
self.ERBlock_6 = old_layer.ERBlock_6
def forward(self, x):
outputs = []
x = self.stem(x)
x = self.ERBlock_2(x)
if self.uses_fuse_P2 and self.fuse_P2:
outputs.append(x)
elif not self.uses_fuse_P2:
outputs.append(x)
x = self.ERBlock_3(x)
outputs.append(x)
x = self.ERBlock_4(x)
outputs.append(x)
x = self.ERBlock_5(x)
outputs.append(x)
if self.uses_6_erblock:
x = self.ERBlock_6(x)
outputs.append(x)
return tuple(outputs)
class DetectV6R2(nn.Module):
"""Efficient Decoupled Head for YOLOv6 R2&R3
With hardware-aware degisn, the decoupled head is optimized with
hybridchannels methods.
"""
# def __init__(self, num_classes=80, anchors=1, num_layers=3, inplace=True, head_layers=None, use_dfl=True, reg_max=16): # detection layer
def __init__(self, old_detect): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = old_detect.nc # number of classes
self.no = old_detect.no # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = old_detect.nl # number of detection layers
if hasattr(old_detect, "anchors"):
self.anchors = old_detect.anchors
self.grid = old_detect.grid # [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl
self.prior_prob = 1e-2
self.inplace = old_detect.inplace
stride = [8, 16, 32] # strides computed during build
self.stride = torch.tensor(stride)
self.use_dfl = old_detect.use_dfl
self.reg_max = old_detect.reg_max
self.proj_conv = old_detect.proj_conv
self.grid_cell_offset = 0.5
self.grid_cell_size = 5.0
# Init decouple head
self.stems = old_detect.stems
self.cls_convs = old_detect.cls_convs
self.reg_convs = old_detect.reg_convs
self.cls_preds = old_detect.cls_preds
self.reg_preds = old_detect.reg_preds
def forward(self, x):
outputs = []
for i in range(self.nl):
b, _, h, w = x[i].shape
l = h * w
x[i] = self.stems[i](x[i])
cls_x = x[i]
reg_x = x[i]
cls_feat = self.cls_convs[i](cls_x)
cls_output = self.cls_preds[i](cls_feat)
reg_feat = self.reg_convs[i](reg_x)
reg_output = self.reg_preds[i](reg_feat)
if self.use_dfl:
reg_output = reg_output.reshape([-1, 4, self.reg_max + 1, l]).permute(
0, 2, 1, 3
)
reg_output = self.proj_conv(F.softmax(reg_output, dim=1))[:, 0]
reg_output = reg_output.reshape([-1, 4, h, w])
cls_output = torch.sigmoid(cls_output)
conf, _ = cls_output.max(1, keepdim=True)
output = torch.cat([reg_output, conf, cls_output], axis=1)
outputs.append(output)
return outputs
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Tool for converting Yolov6 models to the blob format used by OAK",
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
)
parser.add_argument(
"-m",
"-i",
"-w",
"--input_model",
type=Path,
required=True,
help="weights path",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-imgsz",
"--img-size",
nargs="+",
type=int,
default=[640, 640],
help="image size",
) # height, width
parser.add_argument("-op", "--opset", type=int, default=12, help="opset version")
parser.add_argument(
"-n",
"--name",
type=str,
help="The name of the model to be saved, none means using the same name as the input model",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-o",
"--output_dir",
type=Path,
help="Directory for saving files, none means using the same path as the input model",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-b",
"--blob",
action="store_true",
help="OAK Blob export",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-s",
"--spatial_detection",
action="store_true",
help="Inference with depth information",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-sh",
"--shaves",
type=int,
help="Inference with depth information",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-t",
"--convert_tool",
type=str,
help="Which tool is used to convert, docker: should already have docker (https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/) and docker-py (pip install docker) installed; blobconverter: uses an online server to convert the model and should already have blobconverter (pip install blobconverter); local: use openvino-dev (pip install openvino-dev) and openvino 2022.1 ( https://docs.oakchina.cn/en/latest /pages/Advanced/Neural_networks/local_convert_openvino.html#id2) to convert",
default="blobconverter",
choices=["docker", "blobconverter", "local"],
)
args = parser.parse_args()
args.input_model = args.input_model.resolve().absolute()
if args.name is None:
args.name = args.input_model.stem
if args.output_dir is None:
args.output_dir = args.input_model.parent
args.img_size *= 2 if len(args.img_size) == 1 else 1 # expand
if args.shaves is None:
args.shaves = 5 if args.spatial_detection else 6
return args
def export(input_model, img_size, output_model, opset, **kwargs):
t = time.time()
device = torch.device("cpu")
# Load PyTorch model
model = load_checkpoint(
input_model, map_location=device, inplace=True, fuse=True
) # load FP32 model
labels = model.names
labels = labels if isinstance(labels, list) else list(labels.values())
# Update model
for layer in model.modules():
if isinstance(layer, RepVGGBlock):
layer.switch_to_deploy()
for n, module in model.named_children():
if isinstance(module, EfficientRep) or isinstance(module, CSPBepBackbone):
setattr(model, n, YoloV6BackBone(module))
elif isinstance(module, EfficientRep6):
setattr(model, n, YoloV6BackBone(module, uses_6_erblock=True))
elif isinstance(module, CSPBepBackbone_P6):
setattr(
model,
n,
YoloV6BackBone(module, uses_fuse_P2=False, uses_6_erblock=True),
)
model.eval()
for k, m in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(m, Conv): # assign export-friendly activations
if isinstance(m.act, nn.SiLU):
m.act = SiLU()
elif isinstance(m, Detect):
m.inplace = True
model.detect = DetectV6R2(model.detect)
num_branches = len(model.detect.grid)
# Input
img = torch.zeros(1, 3, *img_size).to(device) # image size(1,3,320,320) iDetection
y = model(img) # dry runs
# ONNX export
try:
import onnx
print()
logging.info("Starting ONNX export with onnx %s..." % onnx.__version__)
output_list = ["output%s_yolov6r2" % (i + 1) for i in range(num_branches)]
with BytesIO() as f:
torch.onnx.export(
model,
img,
f,
verbose=False,
opset_version=opset,
input_names=["images"],
output_names=output_list,
)
# Checks
onnx_model = onnx.load_from_string(f.getvalue()) # load onnx model
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # check onnx model
try:
import onnxsim
logging.info("Starting to simplify ONNX...")
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model)
assert check, "assert check failed"
except ImportError:
logging.warning(
"onnxsim is not found, if you want to simplify the onnx, "
+ "you should install it:\n\t"
+ "pip install -U onnxsim onnxruntime\n"
+ "then use:\n\t"
+ f'python -m onnxsim "{output_model}" "{output_model}"'
)
except Exception:
logging.exception("Simplifier failure")
onnx.save(onnx_model, output_model)
logging.info("ONNX export success, saved as:\n\t%s" % output_model)
except Exception:
logging.exception("ONNX export failure")
# generate anchors and sides
anchors = []
# generate masks
masks = dict()
logging.info("anchors:\n\t%s" % anchors)
logging.info("anchor_masks:\n\t%s" % masks)
export_json = output_model.with_suffix(".json")
export_json.write_text(
json.dumps(
{
"nn_config": {
"output_format": "detection",
"NN_family": "YOLO",
"input_size": f"{img_size[0]}x{img_size[1]}",
"NN_specific_metadata": {
"classes": model.nc,
"coordinates": 4,
"anchors": anchors,
"anchor_masks": masks,
"iou_threshold": 0.5,
"confidence_threshold": 0.5,
},
},
"mappings": {"labels": labels},
},
indent=4,
)
)
logging.info("Anchors data export success, saved as:\n\t%s" % export_json)
# Finish
logging.info("Export complete (%.2fs).\n" % (time.time() - t))
def convert(convert_tool, output_model, shaves, output_dir, name, **kwargs):
t = time.time()
export_dir: Path = output_dir.joinpath(name + "_openvino")
export_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
export_xml = export_dir.joinpath(name + ".xml")
export_blob = export_dir.joinpath(name + ".blob")
if convert_tool == "blobconverter":
from zipfile import ZIP_LZMA, ZipFile
import blobconverter
blob_path = blobconverter.from_onnx(
model=str(output_model),
data_type="FP16",
shaves=shaves,
use_cache=False,
version="2022.1",
output_dir=export_dir,
optimizer_params=[
"--scale=255",
"--reverse_input_channel",
"--use_new_frontend",
],
download_ir=True,
)
with ZipFile(blob_path, "r", ZIP_LZMA) as zip_obj:
for name in zip_obj.namelist():
zip_obj.extract(
name,
output_dir,
)
blob_path.unlink()
elif convert_tool == "docker":
import docker
export_dir = Path("/io").joinpath(export_dir.name)
export_xml = export_dir.joinpath(name + ".xml")
export_blob = export_dir.joinpath(name + ".blob")
client = docker.from_env()
image = client.images.pull("openvino/ubuntu20_dev", tag="2022.1.0")
docker_output = client.containers.run(
image=image.tags[0],
command=f"bash -c \"mo -m {name}.onnx -n {name} -o {export_dir} --static_shape --reverse_input_channels --scale=255 --use_new_frontend && echo 'MYRIAD_ENABLE_MX_BOOT NO' | tee /tmp/myriad.conf >> /dev/null && /opt/intel/openvino/tools/compile_tool/compile_tool -m {export_xml} -o {export_blob} -ip U8 -VPU_NUMBER_OF_SHAVES {shaves} -VPU_NUMBER_OF_CMX_SLICES {shaves} -d MYRIAD -c /tmp/myriad.conf\"",
remove=True,
volumes=[
f"{output_dir}:/io",
],
working_dir="/io",
)
logging.info(docker_output.decode("utf8"))
else:
import subprocess as sp
# OpenVINO export
logging.info("Starting to export OpenVINO...")
OpenVINO_cmd = (
"mo --input_model %s --output_dir %s --data_type FP16 --scale=255 --reverse_input_channel"
% (output_model, export_dir)
)
try:
sp.check_output(OpenVINO_cmd, shell=True)
logging.info("OpenVINO export success, saved as %s" % export_dir)
except sp.CalledProcessError:
logging.exception("")
logging.warning("OpenVINO export failure!")
logging.warning(
"By the way, you can try to export OpenVINO use:\n\t%s" % OpenVINO_cmd
)
# OAK Blob export
logging.info("Then you can try to export blob use:")
blob_cmd = (
"echo 'MYRIAD_ENABLE_MX_BOOT ON' | tee /tmp/myriad.conf"
+ "compile_tool -m %s -o %s -ip U8 -d MYRIAD -VPU_NUMBER_OF_SHAVES %s -VPU_NUMBER_OF_CMX_SLICES %s -c /tmp/myriad.conf"
% (export_xml, export_blob, shaves, shaves)
)
logging.info("%s" % blob_cmd)
logging.info(
"compile_tool maybe in the path: /opt/intel/openvino/tools/compile_tool/compile_tool, if you install openvino 2022.1 with apt"
)
logging.info("Convert complete (%.2fs).\n" % (time.time() - t))
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
logging.info(args)
print()
output_model = args.output_dir / (args.name + ".onnx")
export(output_model=output_model, **vars(args))
if args.blob:
convert(output_model=output_model, **vars(args))
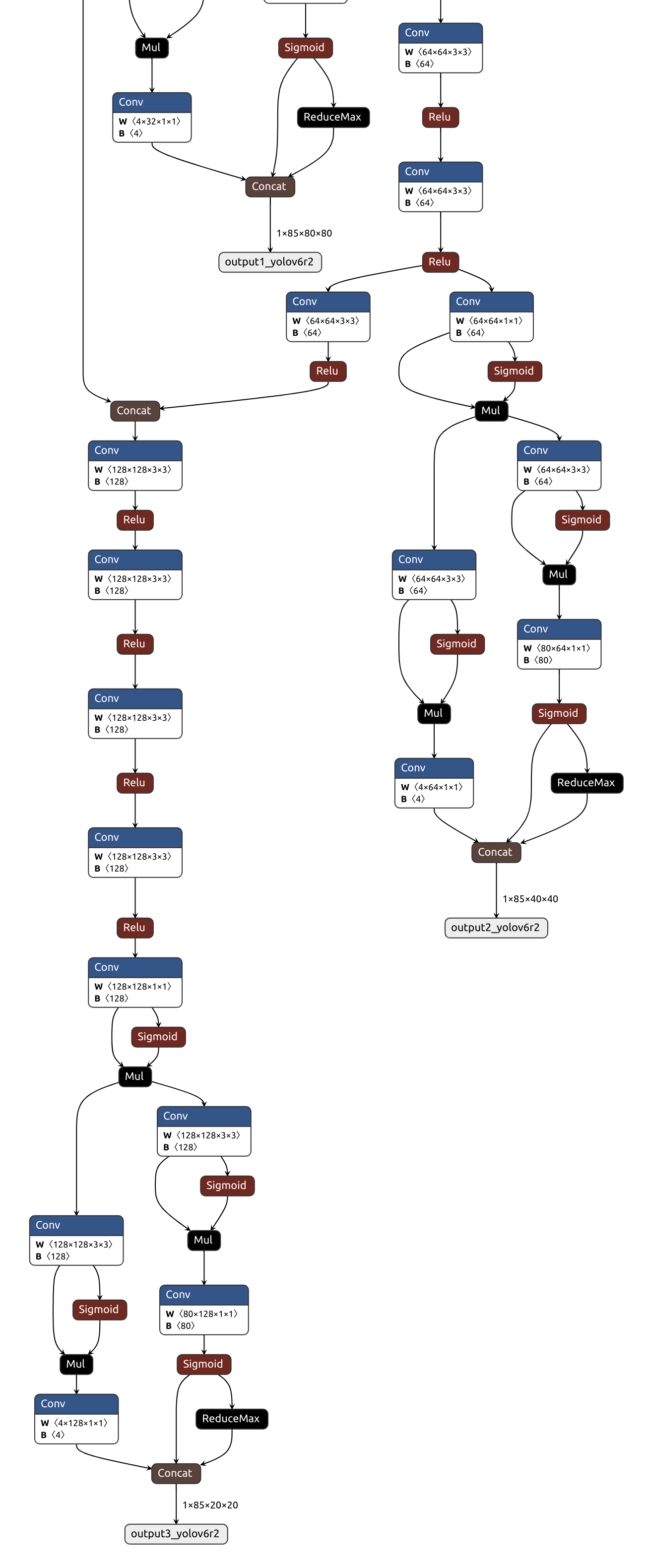
可以使用 Netron 查看模型结构:
▌转换
openvino 本地转换
onnx -> openvino
mo 是 openvino_dev 2022.1 中脚本,
安装命令为
pip install openvino-dev
mo --input_model yolov6n.onnx --reverse_input_channelopenvino -> blob
compile_tool 是 OpenVINO Runtime 中脚本,
<path>/compile_tool -m yolov6n.xml \
-ip U8 -d MYRIAD \
-VPU_NUMBER_OF_SHAVES 6 \
-VPU_NUMBER_OF_CMX_SLICES 6在线转换
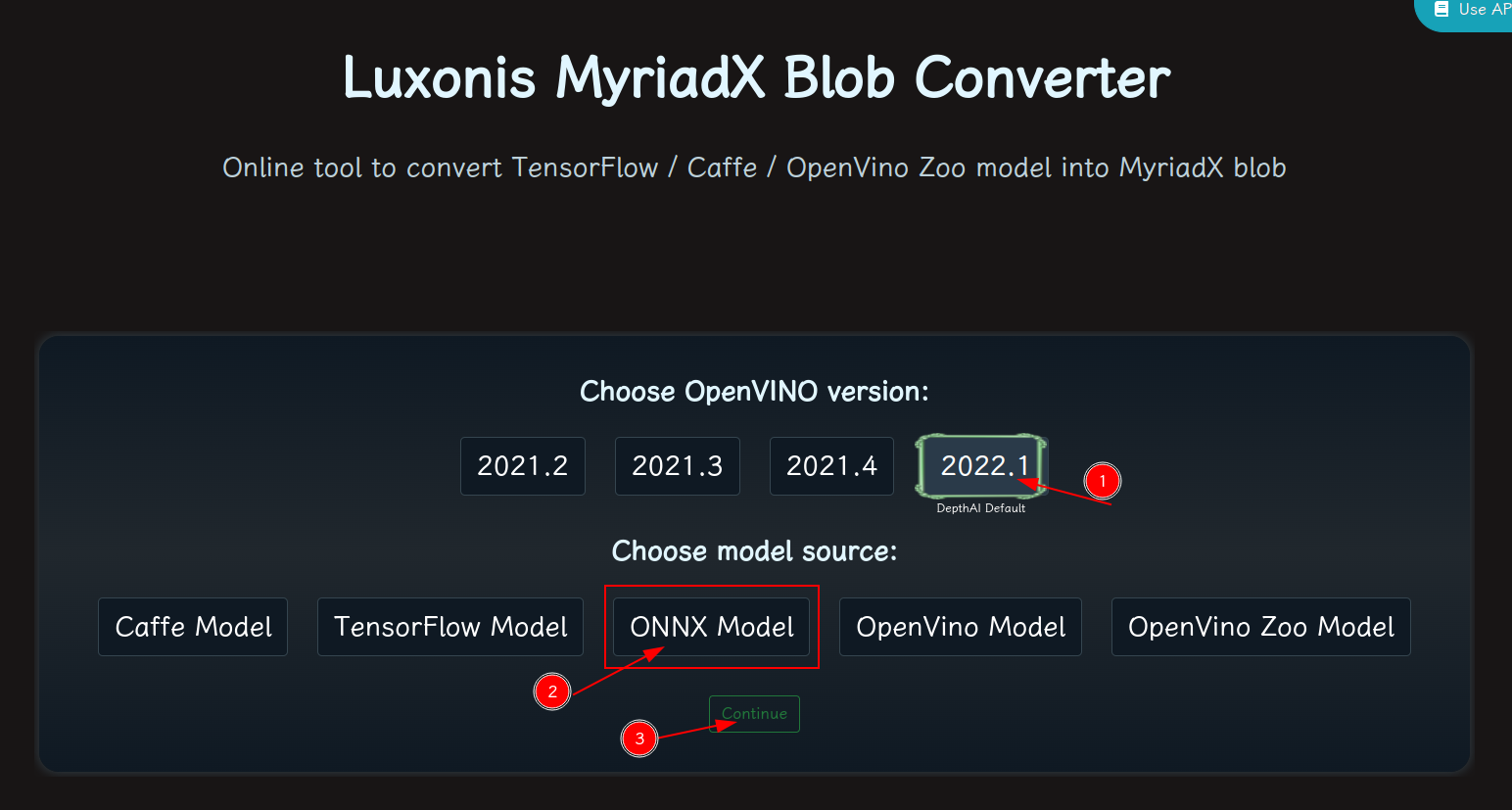
blobconvert 网页 http://blobconverter.luxonis.com/
- 进入网页,按下图指示操作:
- 修改参数,转换模型:
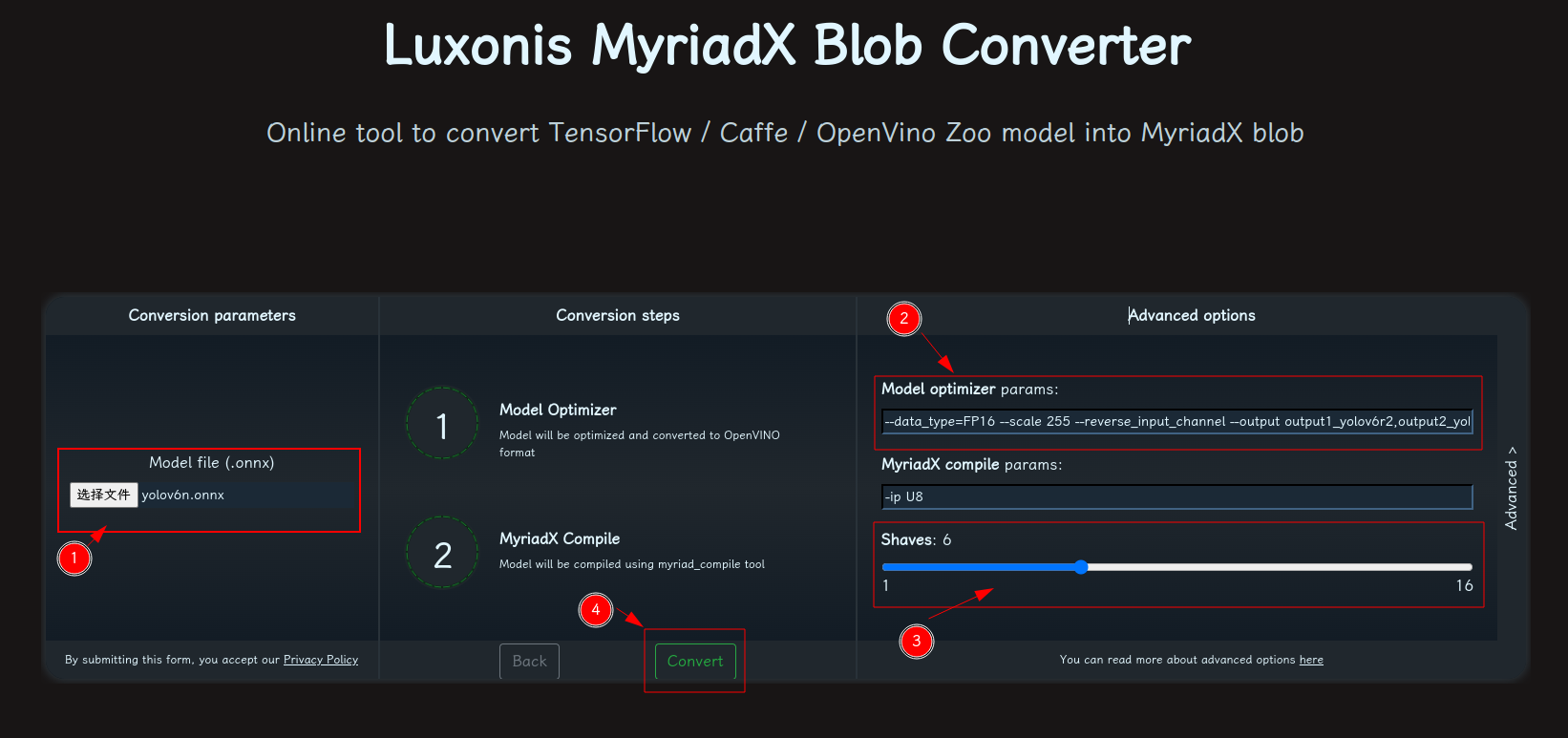
- 选择 onnx 模型
- 修改
optimizer_params为--data_type=FP16 --scale=255 --reverse_input_channel - 修改
shaves为6 - 转换
blobconverter python 代码
blobconverter.from_onnx(
"yolov6n.onnx",
optimizer_params=[
"--scale=255",
"--reverse_input_channel",
],
shaves=6,
)blobconvert cli
blobconverter --onnx yolov6n.onnx -sh 6 -o . --optimizer-params "scale=255 --reverse_input_channel"▌DepthAI 示例
正确解码需要可配置的网络相关参数:
- setNumClasses – YOLO 检测类别的数量
- setIouThreshold – iou 阈值
- setConfidenceThreshold – 置信度阈值,低于该阈值的对象将被过滤掉
# coding=utf-8
import cv2
import depthai as dai
import numpy as np
numClasses = 80
model = dai.OpenVINO.Blob("yolov6n.blob")
dim = next(iter(model.networkInputs.values())).dims
W, H = dim[:2]
output_name, output_tenser = next(iter(model.networkOutputs.items()))
if "yolov6" in output_name:
numClasses = output_tenser.dims[2] - 5
else:
numClasses = output_tenser.dims[2] // 3 - 5
labelMap = [
# "class_1","class_2","..."
"class_%s" % i
for i in range(numClasses)
]
# Create pipeline
pipeline = dai.Pipeline()
# Define sources and outputs
camRgb = pipeline.create(dai.node.ColorCamera)
detectionNetwork = pipeline.create(dai.node.YoloDetectionNetwork)
xoutRgb = pipeline.create(dai.node.XLinkOut)
xoutNN = pipeline.create(dai.node.XLinkOut)
xoutRgb.setStreamName("image")
xoutNN.setStreamName("nn")
# Properties
camRgb.setPreviewSize(W, H)
camRgb.setResolution(dai.ColorCameraProperties.SensorResolution.THE_1080_P)
camRgb.setInterleaved(False)
camRgb.setColorOrder(dai.ColorCameraProperties.ColorOrder.BGR)
# Network specific settings
detectionNetwork.setBlob(model)
detectionNetwork.setConfidenceThreshold(0.5)
# Yolo specific parameters
detectionNetwork.setNumClasses(numClasses)
detectionNetwork.setCoordinateSize(4)
detectionNetwork.setAnchors([])
detectionNetwork.setAnchorMasks({})
detectionNetwork.setIouThreshold(0.5)
# Linking
camRgb.preview.link(detectionNetwork.input)
camRgb.preview.link(xoutRgb.input)
detectionNetwork.out.link(xoutNN.input)
# Connect to device and start pipeline
with dai.Device(pipeline) as device:
# Output queues will be used to get the rgb frames and nn data from the outputs defined above
imageQueue = device.getOutputQueue(name="image", maxSize=4, blocking=False)
detectQueue = device.getOutputQueue(name="nn", maxSize=4, blocking=False)
frame = None
detections = []
# nn data, being the bounding box locations, are in <0..1> range - they need to be normalized with frame width/height
def frameNorm(frame, bbox):
normVals = np.full(len(bbox), frame.shape[0])
normVals[::2] = frame.shape[1]
return (np.clip(np.array(bbox), 0, 1) * normVals).astype(int)
def drawText(frame, text, org, color=(255, 255, 255), thickness=1):
cv2.putText(
frame, text, org, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), thickness + 3, cv2.LINE_AA
)
cv2.putText(
frame, text, org, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA
)
def drawRect(frame, topLeft, bottomRight, color=(255, 255, 255), thickness=1):
cv2.rectangle(frame, topLeft, bottomRight, (0, 0, 0), thickness + 3)
cv2.rectangle(frame, topLeft, bottomRight, color, thickness)
def displayFrame(name, frame):
color = (128, 128, 128)
for detection in detections:
bbox = frameNorm(
frame, (detection.xmin, detection.ymin, detection.xmax, detection.ymax)
)
drawText(
frame=frame,
text=labelMap[detection.label],
org=(bbox[0] + 10, bbox[1] + 20),
)
drawText(
frame=frame,
text=f"{detection.confidence:.2%}",
org=(bbox[0] + 10, bbox[1] + 35),
)
drawRect(
frame=frame,
topLeft=(bbox[0], bbox[1]),
bottomRight=(bbox[2], bbox[3]),
color=color,
)
# Show the frame
cv2.imshow(name, frame)
while True:
imageQueueData = imageQueue.tryGet()
detectQueueData = detectQueue.tryGet()
if imageQueueData is not None:
frame = imageQueueData.getCvFrame()
if detectQueueData is not None:
detections = detectQueueData.detections
if frame is not None:
displayFrame("rgb", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord("q"):
break
